Data generation is a visual representation of data. These representations clearly convey the meaning of data with graphs. According to Business Intelligence (BI), these visual users help make better data-based decisions.
The vision of the data is similar to the architecture. Once you have figured out how to display data, you need to start with the action. (The development, pattern, or important information you are trying to provide at first glance). Then think about the user (how he or she navigates and interacts with data). And only then we can take the last step: make it as clean and beautiful as possible.
Here, are some tips that might be helpful in data visualization:
KPI
They are especially useful if you want to give an immediate idea of how well a company is performing. On a particular production index. Incorporating a simple “gauge” will immediately show you if you are above or below. The target and if you are heading in the right direction. This is especially effective if color-coding included, such as red/green or up / down arrows. You can also draw custom clues and images to give your story a stronger impact.
An index number such as the one at the bottom right is simpler and gives a simple title number. And an indication of how it’s compared to the year/quarter/month before, etc.
Graphs show trends
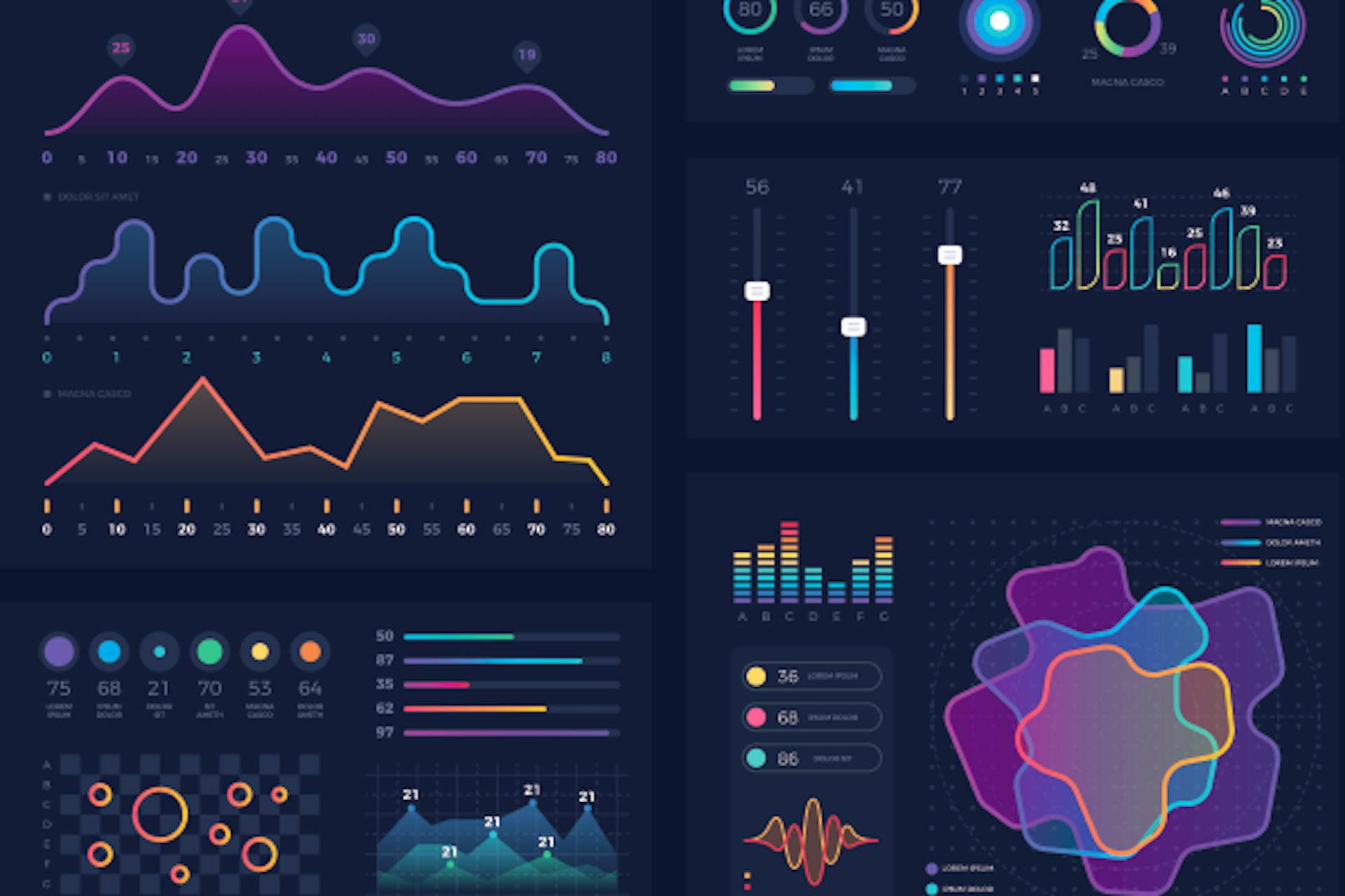
Graphs are very popular in various business cases because they show general trends quickly and accurately. In a way that is difficult to understand. They are especially good for describing trends for different categories at the same time, to help with comparisons. For example, this graph sees sales figures by age group for three different product lines:
Bar charts make things simply broken down
Bar graphs are good for comparing many different values, especially when some of them divided into color code categories. To demonstrate the difference between this and a bar chart, let’s take the same information above and review it again as a bar chart:
Columns compare values side by side
It often makes sense to use a bar chart to compare somewhere with different values. You can also use them to show changes over time. But it makes sense to do so when you want to draw attention to whole numbers instead of the shape of the strategy (which is more effective in graphing).
Pie Charts
Pies easily show the part of each value that consists of the sum. They are intuitive rather than recording only percentages that are up to 100%.
Area
Area maps are useful because they give an idea of the total number and percentage of each category.
Important: This layered rendering is confusing if you enter more than three values in the mix.
This information can reveal things like resource planning, ordering templates, financial management, sharing suitable storage, and more.
Pivot Charts
Pivot charts are not the most beautiful or leading way to predict data. But they are useful if you want to quickly identify key locations by seeing accurate numbers. (Instead of calculating trends), especially if you don’t have access to a self-BI service tool that can do it automatically for you.
Distributed characters: distribution and relationships
The scatter plots represent data categories by round colors and the amount of data by round size. They’re used to predict the distribution and ratio of two variables.
Bubble Charts

Like the scatter plots, the bubble images represent the weight of the values relative to the size of the circular circle. However, they differ in that they compress many different values into one small space and represent only one scale in each class. These are useful if you want to show how a handful of classes are an insignificant class compared to the sea. This visual report makes it easy for users to focus on their biggest challenges or achievements.
Treemaps show hierarchy, compare values
Treemaps are useful for comparing values between hierarchies and between categories and subcategories. And they also allow details to preserved. Immediately highlighting which areas are usually most important.
You achieve this by projecting color-coded rectangles weighted together to reflect their parts as a whole. This treemap shows the values of the different market routes, which are then distributed by country. You can see that AdWords is the most successful channel, but the United States is the most valuable destination of all channels.
Polar tables
A polar image (or polarized image) is a kind of cake. Instead of representing the angles as part of each value of the entity. According to the size of the angle, the angles are the same for all sectors, and the value indicated by how far it reaches the center of the circle.
Area / Scatter maps
With this data visualization, you can instantly see which geographic locations are most important to your company. Data visualized as colored dots on the map; values are expressed by the size of the circle.
This presentation is incredibly useful because it gives you at first glance two important points. Where most of your visitors come from compared to where in the world your most valuable visitors are. Such information may indicate the weaknesses of your marketing strategy in a matter of seconds.
Funnel diagrams
This is a very specific visualization that shows a decrease in values as customers move around the container. The beauty of this is that it enlivens your conversation percentage every step of the way. So you can quickly see where people are falling from the process. The funnel diagram below shows the number of people in all requirements. From the first visit to a website, through each contact point to the last sale.